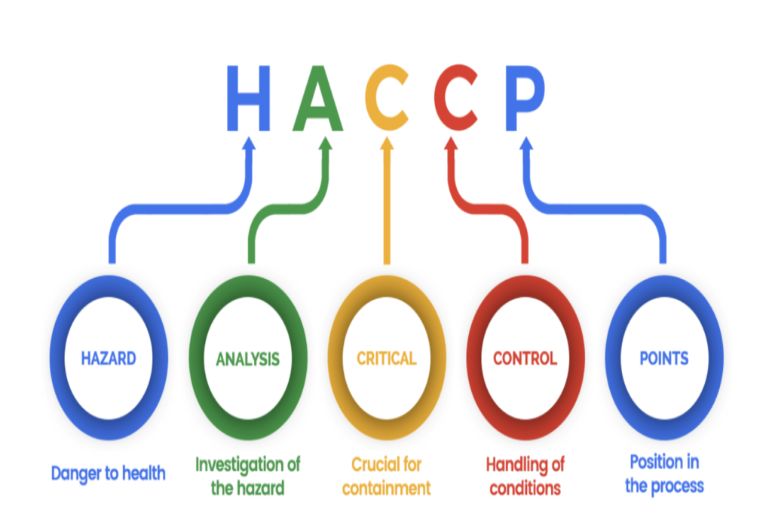
HACCPstands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point. It’s a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production and preparation. Essentially, it’s a management system designed to identify, assess, and control critical points in food production that can cause harm to consumers.
The Core of HACCP

HACCP, a systematic approach to food safety, is rooted in the principle of prevention.
It involves identifying potential hazards—biological, chemical, or physical—that could compromise food safety throughout the food chain. By pinpointing these critical control points (CCPs), businesses can establish precise limits, implement monitoring systems, and define corrective actions to mitigate risks. This proactive methodology ensures that food safety is built into every stage of production, processing, and distribution, shifting the focus from reactive inspection to predictive control. Ultimately, HACCP empowers organizations to deliver safe and wholesome products to consumers with confidence.
HACCP – seven principles
Conducting a Hazard Analysis
A hazard analysis is a systematic process to identify potential hazards within a system or operation.
It involves breaking down activities into steps, identifying potential failures or errors at each step, and evaluating the potential consequences of these failures. This analysis helps uncover risks that could lead to harm, property damage, or environmental impact. By systematically examining the entire process, organizations can implement preventive measures, develop contingency plans, and prioritize risk mitigation efforts. Ultimately, a well-conducted hazard analysis enhances safety, efficiency, and overall system reliability.
Identify the Critical Control Points
Critical Control Points (CCPs) are specific steps in a process where control can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce a food safety hazard to an acceptable level. These points are crucial as they directly impact the safety of the final product. To identify CCPs, a thorough hazard analysis is conducted to determine potential biological, chemical, or physical hazards. The process flow is then examined to pinpoint steps where these hazards can be controlled. A CCP decision tree can be a helpful tool, but expert knowledge is essential. It’s important to remember that not every control point is a CCP; only those steps where control is essential for preventing or reducing a significant hazard qualify. Careful consideration and documentation are key to effective CCP identification.
Establish Critical Limits
Establishing Critical Limits involves identifying and defining the parameters within which a system, process, or resource can operate safely and effectively. These limits serve as guardrails, preventing undesirable outcomes such as failures, breakdowns, or resource depletion. The process demands a thorough understanding of the system’s capabilities, potential stressors, and the consequences of exceeding boundaries. By setting clear and measurable critical limits, organizations can proactively manage risks, optimize performance, and ensure sustainability.
Monitoring Critical Control Points (CCPs)
Monitoring Critical Control Points (CCPs) is a fundamental step in Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) systems. It involves consistently observing and measuring CCPs to ensure they remain under control. This includes establishing specific monitoring procedures, determining critical limits for each CCP, and assigning responsible individuals. Monitoring data must be recorded accurately and promptly to identify deviations from established parameters. Effective monitoring helps prevent hazards from occurring or reaching unacceptable levels, enabling timely corrective actions when necessary. Regular review and analysis of monitoring data are crucial for verifying the system’s effectiveness and making data-driven improvements.
Establishing Corrective Action
Establishing corrective action is a critical component of any robust quality management system.
It involves identifying the root cause of a nonconformity or issue, implementing measures to eliminate the cause, and preventing recurrence. This process typically includes defining the problem clearly, determining its scope and impact, containing the issue to prevent further damage, conducting a thorough root cause analysis, developing and implementing corrective actions, and establishing effective verification processes to monitor the effectiveness of the solution. By systematically addressing and rectifying problems, organizations can enhance product or service quality, reduce risks, improve efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction.
HACCP works alongside other programs
HACCP operates in tandem with other food safety and quality management systems to create a comprehensive approach to food safety. Prerequisite programs, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), establish the foundational hygiene and operational standards necessary for HACCP implementation. Additionally, HACCP complements quality management systems like ISO 9001, providing a structured framework for identifying and controlling food safety hazards. This collaborative approach ensures that all aspects of food production, processing, and distribution are managed effectively, minimizing risks and safeguarding consumer health.
Why is HACCP Important?
HACCP is crucial for ensuring food safety and protecting public health.
By implementing a HACCP system, businesses can:
- Reduce the risk of foodborne illness outbreaks
- Improve product quality and consistency
- Enhance consumer confidence
- Meet regulatory requirements
HACCP is widely adopted by the food industry, from large-scale manufacturers to small-scale food establishments. It is a proactive approach to food safety that helps to build a strong foundation for trust and confidence in the food supply.
Implementing a HACCP System

Implementing a HACCP system can be a complex process, requiring careful planning and commitment from all levels of an organization. Here are the key steps involved:
1. Assemble a HACCP Team
A multidisciplinary team with expertise in food safety, production, and quality assurance is essential.
2. Describe the Product
Clearly define the product, including its intended use, target consumer, and distribution channels.
3. Identify Intended Use and Consumers
Determine how the product will be used and who the target consumers are.
4. Create a Flow Diagram
Develop a detailed diagram illustrating all steps involved in the food production process, from raw materials to the finished product.
5. Conduct a Hazard Analysis
Identify potential biological, chemical, and physical hazards at each step of the process.
6. Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs)
Identify the points in the process where control is essential to prevent or eliminate hazards.
7. Establish Critical Limits
Set specific measurable parameters for each CCP to ensure food safety.
8. Establish Monitoring Procedures
Develop systems to regularly monitor CCPs and ensure compliance with critical limits.
9. Establish Corrective Actions
Determine steps to be taken if monitoring indicates a deviation from critical limits.
10. Establish Verification Procedures
Implement procedures to verify that the HACCP system is working as intended.
11. Establish Record-Keeping Procedures
Document all HACCP procedures, records, and data.
Challenges in HACCP Implementation
While HACCP is a valuable tool, its implementation can face challenges:
- Cost: Developing and maintaining a HACCP system requires time and resources.
- Training: Employees need to be adequately trained in HACCP principles and procedures.
- Cultural Change: Shifting from a reactive to a preventive approach can be challenging.
- Verification and Validation: Ensuring the HACCP system is working effectively requires ongoing effort.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of a well-implemented HACCP system far outweigh the costs, as it contributes to food safety, consumer confidence, and overall business success.
Conclusion
HACCP is a proactive and systematic approach to food safety that has become an industry standard. By identifying potential hazards and implementing controls at critical points in the food production process, HACCP significantly reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses. While implementing and maintaining a HACCP system requires dedication and resources, the benefits in terms of consumer protection, product quality, and regulatory compliance are substantial. As the food industry continues to evolve, HACCP will remain an indispensable tool for ensuring the safety of the global food supply.
Read More :
Featured Image Source: https://tinyurl.com/mrxj77bv

