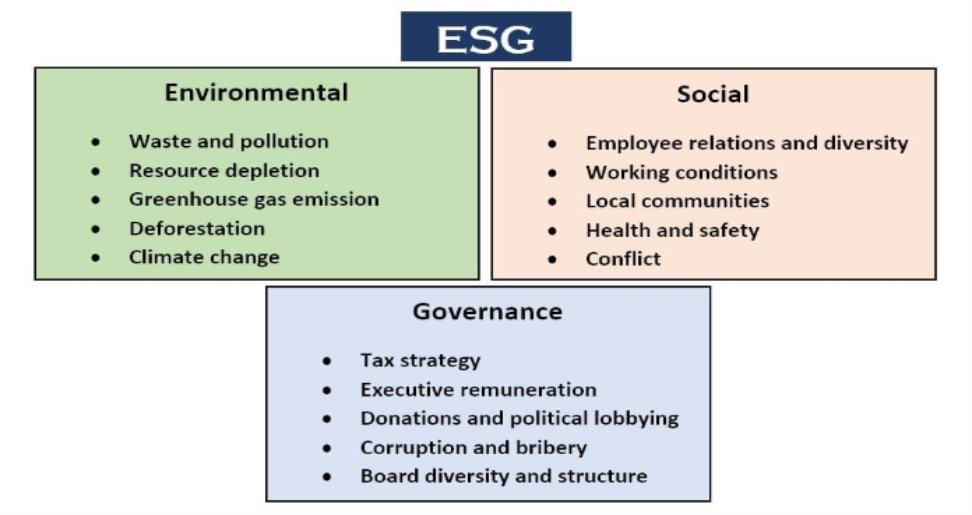
ESG, an acronym that has become increasingly prominent in the business world, stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It refers to a set of standards that businesses must adhere to in order to be considered sustainable and socially responsible. These factors are crucial for assessing a company’s overall impact on society and the environment.
Environmental Factors (E)

The environmental aspect of ESG focuses on a company’s impact on the natural world. Some key environmental factors include:
- Climate change: Climate change, a pressing global concern, refers to the long-term shifts in Earth’s temperature and weather. patterns. Primarily driven by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, climate change has far-reaching consequences. The excessive release of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere traps heat, leading to global warming. This warming, in turn, disrupts natural ecosystems, causes sea levels to rise, and intensifies extreme weather events, including hurricanes, floods, droughts, and heatwaves. The impacts of climate change are felt worldwide, affecting biodiversity, food security, human health, and economic stability. Addressing climate change requires urgent global cooperation, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and adopting sustainable practices to mitigate its effects and ensure a resilient future for generations to come.
- Resource management: Resource management is the effective and efficient use of available resources to achieve organizational goals. It involves planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the utilization of assets, such as human capital, financial resources, technology, and physical assets. By optimizing resource allocation, organizations can improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance. Effective resource management requires a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s needs, capabilities, and constraints, as well as the ability to make informed decisions about resource allocation and utilization.
- Pollution: Pollution is a significant environmental problem that arises from the introduction of harmful substances into the air, water, or land. These pollutants can come from various sources, including industrial activities, transportation, agriculture, and human waste. Air pollution, caused by emissions from vehicles, factories, and power plants, can lead to respiratory problems, acid rain, and climate change. Water pollution, resulting from industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and improper waste disposal, can contaminate drinking water supplies and harm aquatic ecosystems. Soil pollution, often caused by improper waste disposal, industrial activities, and agricultural practices, can contaminate crops and soil organisms. The consequences of pollution are far-reaching, affecting human health, ecosystems, and the overall quality of life. Addressing pollution requires a combination of government regulations, technological advancements, and individual actions to reduce emissions, promote sustainable practices, and protect our planet for future generations.
- Biodiversity: Biodiversity is the term used to describe the variety of life on Earth, encompassing all living organisms from the smallest microorganisms to the largest mammals. It includes the genetic diversity within species, the diversity of species within ecosystems, and the diversity of ecosystems themselves. This intricate web of life is essential for the health of our planet, providing vital ecosystem services like pollination, climate regulation, and water purification. Unfortunately, human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are posing significant threats to biodiversity, leading to species extinction and ecosystem degradation. Protecting biodiversity is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of our planet and the well-being of future generations.
Social Factors (S)

The social aspect of ESG considers a company’s impact on society. Some key social factors include:
- Labor practices: Labor practices refer to the policies, procedures, and conditions that govern the employment relationship between an employer and its employees. These practices encompass a wide range of issues, including hiring and firing policies, working hours, wages and benefits, workplace safety, and employee rights. Labor practices are influenced by various factors such as local laws, industry standards, and corporate culture. Effective labor practices are essential for creating a positive and productive work environment, attracting and retaining talented employees, and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
- Human rights: Human rights are fundamental entitlements that belong to every person, regardless of nationality, ethnicity, religion, gender, or any other characteristic. They are inalienable, meaning they cannot be taken away. These rights are essential for human dignity and well-being. They encompass a wide range of freedoms and protections, including the right to life, liberty, and security of person; freedom from torture, cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment; freedom of expression and opinion; the right to work and education; the right to adequate food, clothing, and housing; and the right to participate in cultural and political life. Human rights are enshrined in international law, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and are protected by various national and regional legal frameworks. While significant progress has been made in promoting and protecting human rights, numerous challenges and violations persist worldwide. Efforts to advance human rights require collective action, advocacy, and respect for the inherent dignity of all individuals.
- Community engagement: Community engagement is the active and ongoing process of involving individuals and groups in the decision-making and implementation of initiatives that affect their lives. It fosters a sense of ownership, collaboration, and empowerment within a community. Effective community engagement involves active listening, open communication, and building trust between community members and organizations. By involving community members in the planning and implementation of projects, organizations can ensure that their efforts are aligned with the needs and priorities of the community they serve, leading to more sustainable and impactful outcomes.
- Product safety: Product safety is a paramount concern for consumers and manufacturers alike. It encompasses a wide range of measures designed to ensure that products are free from defects or hazards that could cause harm or injury. These measures typically involve rigorous testing, quality control procedures, and adherence to safety standards and regulations. By prioritizing product safety, manufacturers can protect their customers, maintain brand reputation, and minimize legal liabilities. Moreover, ensuring product safety contributes to a safer and more trustworthy marketplace, fostering consumer confidence and overall well-being.
Governance Factors (G)

The governance aspect of ESG focuses on a company’s internal management and operations. Some key governance factors include:
- Corporate governance: Corporate governance refers to the framework of rules, practices, and procedures that regulate how a company is managed and controlled. It encompasses the relationship between the company’s board of directors, management, shareholders, and other stakeholders. Effective corporate governance ensures transparency, accountability, and fairness in decision-making, ultimately protecting the interests of all stakeholders. It involves setting clear objectives, establishing ethical standards, and implementing internal controls to prevent fraud and mismanagement. Corporate governance also fosters trust and confidence among investors, employees, customers, and the broader community.
- Board of directors: A board of directors is a governing body that oversees the operations of a company. Composed of individuals elected or appointed by shareholders, the board ensures that the company is managed in the best interests of its owners. Their responsibilities typically include setting strategic direction, approving major decisions, monitoring financial performance, hiring and evaluating the CEO, and ensuring compliance with laws and regulations. Boards play a crucial role in maintaining corporate governance and accountability, safeguarding the interests of stakeholders, and guiding the company toward long-term success.
- Executive compensation: Executive compensation refers to the financial rewards and benefits provided to high-level management in exchange for their contributions to an organization’s success. This compensation typically includes a base salary, bonuses, stock options, retirement plans, and other perks. The goal of executive compensation is to attract and retain top talent, incentivize performance, and align the interests of executives with those of shareholders. However, the topic of executive compensation has been a subject of much debate and controversy, with concerns raised about the vast disparities between executive pay and the wages of ordinary workers. The level of executive compensation is often determined by factors such as the company’s size, industry, performance, and the specific role of the executive.
- Corruption and bribery: Corruption and bribery, two intertwined evils that undermine the fabric of society, have become pervasive in many countries worldwide. Corruption, in its broadest sense, refers to the misuse of power for personal gain, often involving illegal or unethical activities. Bribery, a specific form of corruption, involves the giving or receiving of valuable items or favors in exchange for preferential treatment or services. These practices have far-reaching consequences, eroding trust in institutions, hindering economic development, and exacerbating inequality. Corruption and bribery can lead to a decline in public services, as resources are diverted for personal enrichment, and can also foster a culture of impunity, where those in power feel untouchable. Moreover, these practices can create a vicious cycle, as corrupt officials may demand bribes to facilitate business or obtain permits, leading to increased costs for businesses and consumers. Ultimately, corruption and bribery undermine the principles of good governance and hinder the progress of a nation.
Read More :
Featured Image Source: https://tinyurl.com/ydr8d4uw